How to do a competitive analysis for local SEO
When it comes to local SEO, there is a lot of noise.
From the latest industry buzz to the nuances of a specific website, a strategic to-do list can quickly become inundated with tasks that don’t consider the big picture.
However, none of these tasks matter if you ignore the competitors.
A competitive analysis for local SEO can uncover:
By understanding the effort and focus used by those who rank well locally, you can thrive in even the most competitive search environments.
Determining your local competitors
Local SEO competitors require a different approach than competitors in national markets.
In a national SEO campaign, competitors typically target hundreds or thousands of keywords. At the local level, most competitors tend to target somewhere between 20 and 100 keywords.
Local SEO typically has fewer keywords because it is defined by your physical community.
Local SEO is designed to support a network of small businesses, franchises, and physical goods and services. Unlike national SEO, there is no cloud-based or SaaS architecture or leading national e-commerce website.
Dealers, professionals and local businesses offer a service or item that customers will receive in their community. The products and services of these companies are limited to the parameters of their local population. If a local business offers garage door repairs, demand is limited to the number of people who need garage door repairs in that community.
Because local SEO is limited to a physical community, discovering competitors is simple. Identify 5-10 core keywords and see who ranks first.
However, competitive analysis for local SEO gets complicated quickly when there is more than one location for the business. Each location poses unique challenges.
Although local competitive analysis considers a smaller portion of keywords, the complexities of local search affect these keywords.
3 steps to conducting a competitive analysis for local SEO
A competitive analysis for local SEO considers keyword search visibility in the context of three local ranking factors:
1. Compare proximity
Are you further from the city center than your main competitors? Is this location information important to you? After all, it’s not like you can move locations for the sake of SEO.
Understanding your location in the context of your competitor’s location is important because proximity could answer why they rank first.
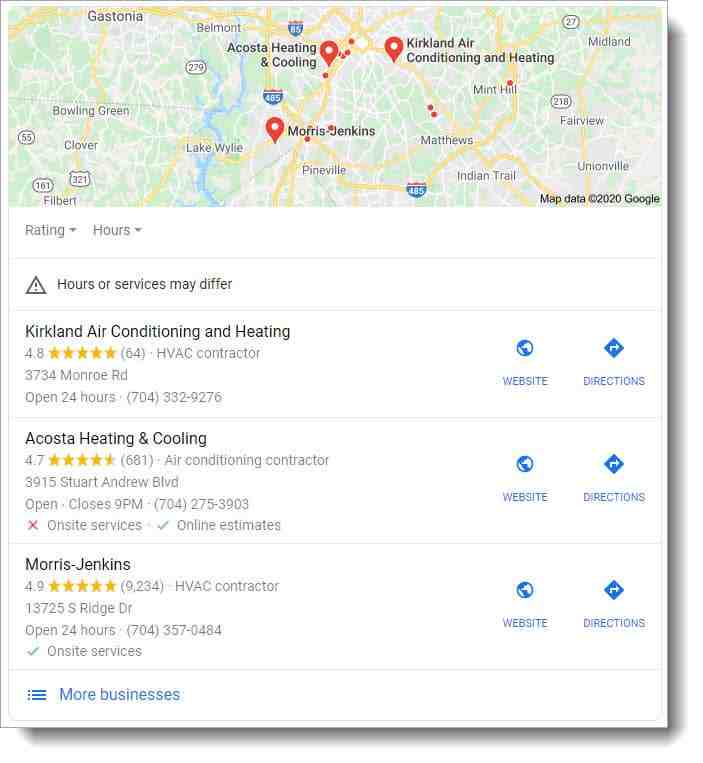
In the image below, a search for “Kansas City Defense Attorney” a highly desirable keyword for Kansas City Defense Attorneys, the #1 ranking is occupied by a law firm located in 0.2 miles from downtown Kansas City. Business #2 is located 3.1 km from the city center.
A quick search for your primary keyword can indicate whether proximity will affect your campaign. Check the distance between the verified location and the city center for the #1 ranking in GBP (aka, your competitor) in the local package. Then compare your competitor’s distance to the distance between your verified location and the city center.
If you’re a Service Area Business (SAB), chances are your competitors are also SAB, which means you won’t be able to check the distance between their address and the city centre. In these scenarios, you should still consider the distance between your verified location and the city center.
If your website struggles to achieve local ranking growth in the future, proximity could be limiting progress. Sometimes your verified address will be too far from your target location to rank, which means you may need to change your target location.
During a competitive analysis for local SEO, a quick check of the proximity of competitors is enough to understand how much distance matters in your specific market. However, from this initial check, you may determine that a deeper understanding of your proximity would help you frame your strategy.
If a more comprehensive proximity analysis can help, consider completing a full proximity audit as a next step. For example, you might consider a full proximity audit if you look at the distance, GBP, and strategy on the page, but you still can’t determine why a competitor is ranking well. The Proximity Audit is a deeper analysis of all the factors that affect proximity-based rankings in a specific market.
2. Assess GBP optimization
In local SEO, Google Business Profile is the star of the show. Everyone is vying for that #1-3 position in the local pack. Competitors tend to pay more attention to GBP with their local SEO strategy because this profile appears directly at the top of search results.
Evaluate the following ranking factors in your competitors’ GBP listings and compare your own profile:
The name, main category and reviews are directly visible on the profile, but to see additional GBP categories for a business you will need a tool like GMB Everywhere. Here are the key ranking factors on Google Business Profile, but it’s also important to see how much your competitors have invested in additional GBP features:
If competitors are ranking based on reviews and proximity alone, some adjustments to your GBP categories can improve your local pack ranking. But if a #1 competitor has filled out their profile with all the details and is posting every week, it’s likely going to take a substantial effort to beat them.
Ultimately, a Google Business Profile aims to update users with as much information about the business as possible. Rankings are great, but keeping customers informed about your business is a solid practice across all communication channels.
3. Analyze on-page content
On-page SEO is an important ranking signal for the local package. So what does the #1 competitor’s website look like? Click the Website button that appears directly in the local package to get started.
While analyzing competitor websites, you will typically see two types of sites linked from GBP:
The content of a home page is often structured differently than the content of a location page:
Review your competitor’s homepage or location page to determine how much effort is required with your website. How much has your competitor invested in their website and/or location page?
Here are some questions to review for a homepage or location page linked from GBP.
These questions are not exhaustive, but they are a good starting point and can help you understand the level of investment and strategy behind a competitor’s website.
Compiling the information and looking at the big picture
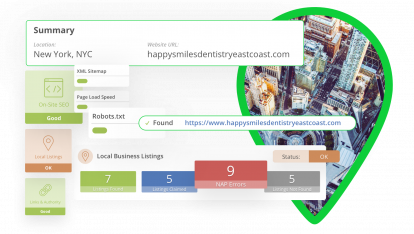
You have collected information about a competitor’s proximity, GBP and website. Now, it’s time to analyze this information and come up with your local SEO strategy.
Here’s an example of what we might learn about a #1 “Houston dentist” competitor.
In the above example of competitive analysis for local SEO, we can see that our business needs several improvements to compete for that #1 ranking, from updating the GBP category to considering video content.
The best local SEO strategy is unique to its marketplace
This market includes competitors who have invested varying amounts of content optimization, links, and even physical real estate. While there will always be a list of SEO tasks, a competitive analysis can help determine which tasks will have the greatest impact.
The views expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
Harmony Huskinson is an SEO Strategist at Portent, a full-service digital marketing agency. Harmony specializes in local SEO and has worked with hundreds of businesses since she began her digital marketing career in 2015. You can find Harmony on Twitter or LinkedIn to chat about the intersection of community and digital in local spaces.
What are the 5 competitive strategies?
5 types of competitive strategy
- Cost leadership. A cost leadership strategy keeps the prices of products and services lower than those of the competition to encourage customers to buy lower-priced products to save money. …
- Product differentiation. …
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)…
- Cost approach. …
- Commitment to customer strategy.
What are the 3 competitive strategies? According to Porter’s generic strategies model, there are three basic strategic options available to organizations to gain competitive advantage. These are: Cost Leadership, Differentiation and Focus.
What is the first step in competitor analysis?
The first step in doing a competitive analysis is to identify your competitors. There are two types of competitors: direct and indirect. A direct competitor is one that offers the same product or service and targets the same customer base as your business.
What are the steps of competitor analysis? Competitive analysis is the process of researching, categorizing, and evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of brands that you consider a potential threat to your business. By conducting a competitive analysis, you will gain knowledge and understanding of: The market in which you operate. Your target audience.
What is a competitive analysis in a business plan?
Competitive analysis means evaluating and analyzing the comparative strengths and weaknesses of competitors; they may include your current and potential product and service development and marketing strategies. For more information on how to analyze your competition, see: How to write the competition section of your business plan.
What’s in a Competitive Analysis? A competitive analysis is a strategy that involves researching major competitors to gain insights into their products, sales, and marketing tactics. Implementing stronger business strategies, keeping competitors at bay, and capturing market share are just some of the benefits of conducting a competitive market analysis.
What is Porter’s 5 Forces analysis example?
Five Forces Analysis Live Example The five forces are the threat of new market players, the threat of substitute products, the power of customers, the power of suppliers, industry rivalry that determines competitive intensity and the attractiveness of a market
What to understand by Porter’s five forces, explain with an example? These forces include the number and power of a firm’s competitive rivals, potential new market entrants, suppliers, customers, and substitute products that influence the firm’s profitability. Five forces analysis can be used to guide business strategy to increase competitive advantage.
What is the main goal of the Porter’s 5 forces analysis?
The purpose of Porter’s five forces model is to assess the overall competitive landscape of a particular business sector. Each of these five forces corresponds to a key component of market intensity.